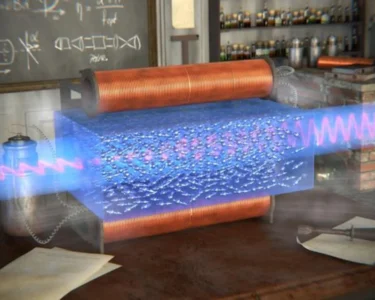
In a groundbreaking development, South Korean scientists have created an artificial muscle that is 4,000 times stronger than its own weight, marking a major milestone in the field of biomechanics and robotics. This new advancement has the potential to revolutionize industries ranging from robotics to healthcare by enabling the creation of robots and prosthetics with unprecedented power-to-weight ratios. In this blog, we’ll dive into the science behind this remarkable achievement, its potential applications, and what it could mean for the future of robotics and human augmentation.
1. What is the Artificial Muscle?
The artificial muscle created by South Korean researchers is a synthetic material designed to mimic the functionality of natural muscles. Unlike traditional actuators or motors, which can be bulky and inefficient, this artificial muscle is incredibly lightweight and flexible, making it ideal for use in delicate applications that require precision and strength. The material is made from a unique combination of polymers and carbon nanotubes that respond to electrical stimuli, similar to how biological muscles contract and relax.
This breakthrough is notable because the artificial muscle can generate a significant amount of force relative to its size, making it 4,000 times stronger than its own weight. This strength-to-weight ratio is far superior to anything seen in previous artificial muscle designs, which were often limited by the mechanical properties of the materials they used.
2. How Does the Artificial Muscle Work?
The new artificial muscle operates based on the principles of electroactive polymers. When an electric current is passed through these polymers, they expand and contract, mimicking the way natural muscles work. In this case, the addition of carbon nanotubes enhances the material’s ability to withstand tension and stress, making it incredibly durable while maintaining flexibility.
The researchers have designed the muscle to be both lightweight and highly efficient, with a much faster response time compared to other artificial muscles. Unlike traditional electric motors or hydraulic actuators, this muscle doesn’t rely on heavy components or complex mechanical systems. Instead, it works by leveraging the electrical stimulation of its molecular structure to produce force and movement, offering more precise control in a lightweight form.
3. Why is Strength-to-Weight Ratio Important?
One of the main advantages of this artificial muscle lies in its strength-to-weight ratio. In both robotics and medical prosthetics, the ability to generate significant power without adding excess weight is crucial. For example, in robotic systems, excessive weight can lead to inefficient energy consumption and slower movements, limiting the overall performance of the robot. With this new artificial muscle, robots and prosthetic devices can achieve greater strength and flexibility while maintaining a lightweight design.
In the case of biomechanics, a muscle that is both strong and light can significantly improve the functionality and comfort of wearable devices. Prosthetics, for example, could be made to mimic natural human movements with much greater precision and efficiency, potentially improving the quality of life for people with limb loss.
4. Potential Applications in Robotics
One of the most promising areas for the use of this artificial muscle is in robotics. The technology could be applied to create robots that are not only more agile and faster but also more efficient and versatile. Traditional robotic actuators tend to be bulky and heavy, which can restrict the robot’s movement and increase its energy consumption. By replacing these heavy components with lightweight, powerful artificial muscles, robots could perform tasks with greater speed and precision.
Moreover, the use of this artificial muscle could lead to robots that can perform a wider range of tasks. For example, robots designed for search and rescue operations, surgical assistance, or space exploration could benefit from the muscle’s ability to replicate human-like dexterity and strength. In these environments, the combination of strength, lightweight construction, and agility is essential for effective performance.
5. Impact on Prosthetics and Human Augmentation
In addition to robotics, the creation of this artificial muscle has profound implications for prosthetics and human augmentation. Prosthetic limbs have come a long way in recent years, with many models now capable of mimicking the function of natural limbs. However, current prosthetics still face limitations in terms of strength, range of motion, and comfort.
This artificial muscle could play a key role in overcoming some of these challenges. By incorporating the muscle into prosthetics, manufacturers could create limbs that are more responsive and capable of generating greater force, all while remaining lightweight and comfortable for the wearer. For individuals with disabilities, this could lead to prosthetics that more closely resemble and function like natural limbs, improving both mobility and quality of life.
Furthermore, in the field of human augmentation, this artificial muscle could be used to enhance physical capabilities. Exoskeletons, for instance, could be developed to augment human strength and endurance, allowing individuals to perform tasks that would otherwise be too physically demanding. The technology could be used in military applications, rehabilitation, or even enhancing human athletic performance.
6. Challenges and Limitations
Despite its immense potential, this artificial muscle is not without its challenges. One of the primary issues that researchers must address is ensuring the long-term durability of the material. While the muscle is strong and flexible, it needs to withstand repeated use and remain functional over time without degrading.
Additionally, while the artificial muscle can generate great force relative to its size, there are still questions about its scalability. For larger robots or prosthetic limbs, the material would need to be adapted to handle larger loads without sacrificing performance. Researchers will also need to develop efficient systems for powering the artificial muscles, as they require electrical stimulation to function.
7. The Future of Artificial Muscles in Technology
The development of this 4,000 times stronger-than-its-weight artificial muscle represents a revolutionary step forward in the field of biomechanics and robotics. As the technology advances, we can expect to see even more powerful and efficient versions of these muscles, opening up new possibilities in a variety of fields.
In the future, artificial muscles could lead to the creation of smarter, more efficient robots, as well as biomechanical devices that seamlessly integrate with the human body. With the combination of strength, precision, and lightweight design, the applications for this technology are virtually limitless, from medical treatments to industrial automation.
Conclusion: A Leap Toward the Future of Robotics and Prosthetics
The creation of an artificial muscle that is 4,000 times stronger than its weight by South Korean scientists marks an incredible breakthrough in technology. Its potential to revolutionize robotics, prosthetics, and human augmentation is immense. Although there are still challenges to overcome, such as durability and scalability, the future of this technology looks bright. With continued research and development, we could soon see robots and prosthetic devices that are not only stronger but more efficient, agile, and human-like than ever before.
This advancement in artificial muscle technology is a game-changer, paving the way for the next generation of robotics and biomechanics. As the field progresses, it may soon be a key component in transforming industries and improving lives in ways we can only imagine today.