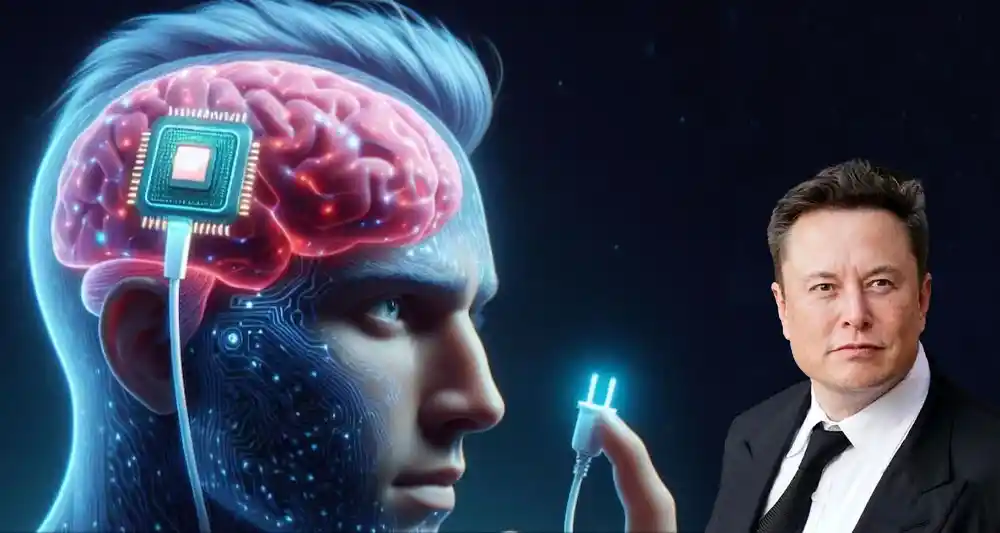
Advancements in neuroscience and technology are accelerating at an unprecedented rate, and one of the most exciting developments is the creation of a neural implant that is smaller than a grain of salt. This ultra-miniature device can wirelessly transmit brain activity data, offering immense potential for both medical research and the development of next-generation brain-computer interfaces (BCIs). In this blog, we’ll dive into the groundbreaking technology behind this neural implant, its possible applications, and what it could mean for the future of human health and technology.
1. What is the “Smaller Than a Grain of Salt” Neural Implant?
The new neural implant, developed by scientists and engineers, is a highly sophisticated device designed to monitor and wirelessly transmit brain activity. What sets it apart from existing technology is its unprecedented size—it is, in fact, smaller than a grain of salt. This minuscule size enables it to be implanted into the brain with minimal invasiveness, making it an ideal tool for long-term monitoring without causing significant discomfort or damage.
The implant is designed to record electrical signals produced by the brain, which are then sent wirelessly to external devices. With this ability, it opens up exciting new possibilities in the fields of neuroengineering, neurology, and even neuroprosthetics.
2. How Does the Neural Implant Work?
The core functionality of the implant relies on its ability to capture brain activity and wirelessly transmit it to a receiver. The device is equipped with sensors that can detect electrical impulses generated by neurons in the brain. These signals are then transmitted to a receiver—usually a wearable or mobile device—using wireless communication protocols, such as Bluetooth or Wi-Fi.
One of the most remarkable features of the implant is its low power consumption, which allows it to operate for extended periods without needing a frequent recharge. The wireless transmission of brain data also eliminates the need for bulky cables, further enhancing the implant’s functionality and ease of use.
3. Revolutionizing Medical Applications
The potential medical applications of this tiny neural implant are immense. For instance, it could offer real-time monitoring of patients with neurological disorders such as epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease, or Alzheimer’s disease. By tracking and transmitting brain activity, doctors could gain deeper insights into a patient’s condition, enabling more accurate diagnoses and personalized treatment plans.
Moreover, this technology could also be used in the development of advanced prosthetics. By capturing brain signals, it may be possible to control prosthetic limbs or assistive devices directly with the user’s thoughts. This would mark a significant step toward the development of brain-computer interfaces that enable patients to interact with the world in a more natural and intuitive way.
4. The Role of Wireless Technology in Brain-Computer Interfaces
At the heart of this neural implant is its wireless transmission capability, a feature that is critical for its success and widespread adoption. Traditional neural implants often relied on wired connections, which posed a number of challenges, including limited mobility, risk of infection, and increased invasiveness.
By making the device wireless, scientists have overcome many of these obstacles. Now, individuals wearing the implant can move freely and without restrictions, while still receiving constant, real-time updates on their brain activity. This wire-free approach also makes the device less prone to failure or damage due to external factors, such as physical trauma or accidental pulls on wires.
5. Potential for Enhanced Brain Research and Neurofeedback
Another area where this neural implant could make a huge impact is in brain research. Scientists have long been working to decode the complex signals generated by the brain, and this implant could provide an invaluable tool for this purpose. By providing an accurate, real-time picture of brain activity, researchers could better understand how different areas of the brain work together and how various cognitive functions are processed.
In addition to its research applications, the implant could be used for neurofeedback—a therapeutic technique that helps individuals regulate their brain activity. Neurofeedback has been shown to help with conditions like ADHD, anxiety, depression, and even insomnia. With continuous, precise data on brain activity, the implant could offer even more effective neurofeedback treatments, allowing users to achieve better mental well-being over time.
6. Security and Privacy Concerns: What Needs to Be Addressed?
While the potential of this neural implant is incredibly exciting, it also raises important concerns about privacy and security. Since the implant transmits sensitive brain data wirelessly, it’s essential to ensure that this information is protected from unauthorized access. Hackers could potentially intercept or manipulate brain activity data, leading to serious ethical and security implications.
To address these concerns, researchers are working on incorporating advanced encryption and security protocols to safeguard the data. Additionally, as the technology evolves, regulatory frameworks and ethical guidelines will need to be established to ensure that these devices are used responsibly and securely.
7. The Future of Neural Implants and Brain-Computer Interfaces
As we look to the future, the possibilities for neural implants and brain-computer interfaces seem endless. The integration of these tiny, wireless devices with other technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI) and augmented reality (AR), could lead to innovations that were once thought to be the stuff of science fiction.
For example, brain activity could one day be used to control everything from smart home devices to virtual environments. Additionally, as these implants become more refined and widely adopted, we could see the development of advanced neuroprosthetics that can restore full mobility or cognitive function in patients with severe disabilities.
With this neural implant, we are entering a new era in which the boundaries between the human brain and technology are becoming increasingly blurred. As this technology evolves, it holds the potential not only to transform healthcare but to reshape the very way we interact with the world around us.
Conclusion: A New Frontier in Neuroscience and Technology
The development of a neural implant that is smaller than a grain of salt and capable of wirelessly transmitting brain activity data marks a major milestone in both neuroscience and technology. Its applications in medical treatments, brain research, and neurofeedback are just the beginning. While there are still challenges to address—particularly around security and privacy—the possibilities for this tiny, yet powerful device are truly exciting.
As research continues and technology advances, we can expect to see even more remarkable innovations that bridge the gap between the brain and machines, ultimately leading to profound changes in how we live, work, and interact with the world. The future of brain-computer interfaces and neural implants is indeed promising, and it’s only a matter of time before these groundbreaking devices become commonplace in both medical and consumer applications.